
Other Vitamin B Foods
- Top 10 Foods Highest in Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
- Top 10 Foods Highest in Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
- Top 10 Foods Highest in Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
- Top 10 Foods Highest in Vitamin B6
- Top 10 Foods Highest in Vitamin B9 (Folate)
- Top 10 Foods Highest in Vitamin B12

Other Vitamin B Foods

Health Benefits of Niacin (Vitamin B3)
- Protect Against Heart Disease - Niacin is prescribed pharmacologically to lower LDL fats and triglycerides by preventing the breakdown of fats into these individual components. Niacin consumed at such high levels can cause rashes, headaches, nausea, and diarrhea. Consult your doctor before taking niacin supplements in high doses.(2,3)
- Regulation of Blood Sugar and Insulin Dependence (*Controversial) - Studies suggest that vitamin B3 (niacin) can help decrease insulin sensitivity,(4) however, other studies find no difference.(5) Niacin has also been shown to help alleviate some of the destructive autoimmune reactions of type I diabetes, and further studies are being conducted to assess its effectiveness.(5)
- Reduced Cancer Risk - Studies show that niacin reduces cancer risk by ensuring DNA integrity and maintenance, and through proper regulation of the tumor suppressor gene: p53.(6-8)
- Slow the progression of AIDS - An observational study has reported slowing the progression of AIDS and increasing survival with high doses of niacin.(9)
People at Risk of a Niacin (Vitamin B3) Deficiency
- People with HIV/AIDS - The body's immune system creates a specific cytokine, interferon gamma, which breaks down tryptophan, a precursor of niacin. Studies show that HIV patients who take increased levels of niacin slow the progression of AIDS.(9-11)
- People who eat high amounts of refined foods - Bran, which is high in vitamin b3, is typically removed during any refining process. Anyone who eats high amounts of white bread, white rice, corn syrup, or other refined products will not receive adequate amounts of niacin. Even though most of these foods are now fortified, it is still best to eat unrefined food products.
Other Vitamin B Foods

High Risk Groups for a Vitamin B6 Deficiency
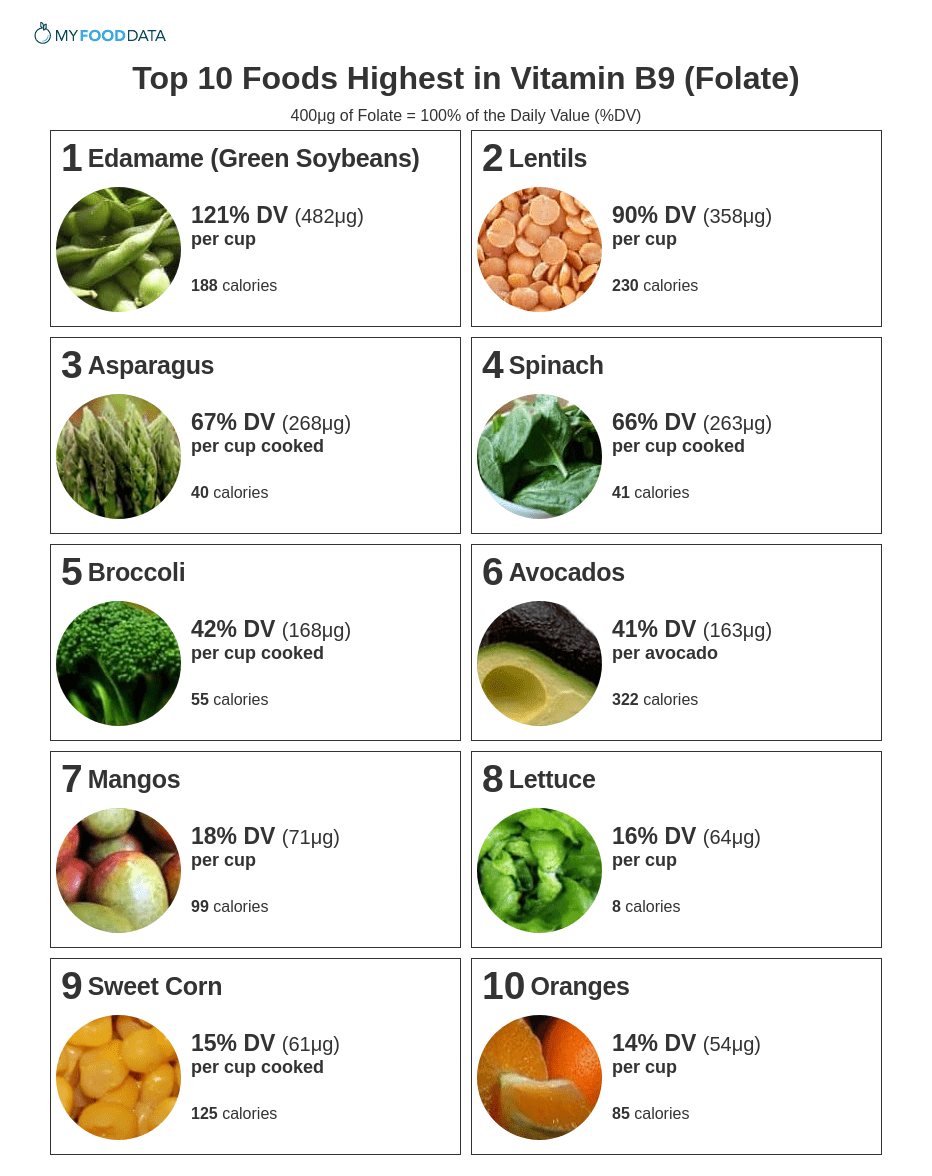
How Much Folate Do You Need?
The current daily value (%DV) for folate is 400μg per day (2) and is meant as a general measure for all people. The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) and adequate intake (AI) are more refined measures which account for age and life situation. (1)
In the case of folate, the DV is much higher than the AI and RDA to

High Risk Groups for a Vitamin B6 Deficiency


Comments
Post a Comment